Threat intelligence is the analysis of data using tools and techniques to generate meaningful information about existing or emerging threats targeting the organization that helps mitigate risks. Threat Intelligence helps organizations make faster, more informed security decisions and change their behavior from reactive to proactive to combat the attacks.
What is cyber threat intelligence and why do you need it?
Cyber Intelligence is the knowledge that allows you to prevent or mitigate cyber-attacks by studying the threat data and provide information on adversaries. It helps to identify, prepare, and prevent attacks by providing information on attackers, their motive, and capabilities.
Threat intelligence prepares organizations to be proactive with predictive capabilities instead of reactive for future cyber-attacks. Without understanding security vulnerabilities, threat indicators, and how threats are carried out, it is impossible to combat cyber-attacks effectively. Using cyber intelligence security professionals can prevent and contain attacks faster, potentially saving the cost in the event of cyber-attacks. Threat intelligence can elevate enterprise security at every level, including network and cloud security.
What Does Threat Intelligence Do?
Threat intelligence helps organizations with valuable knowledge about these threats, build effective defense mechanisms, and mitigate the risks that could cause financial and reputational damage. Threat Intelligence is the predictive capability to defend the future attacks that the organization is exposed to so they can proactively tailor their defenses and preempt future attacks.
Who is A Cyber Threat Intelligence Analyst?
Threat Intel and the Art of War: Why Knowing Yourself Isn’t Enough
What Are The Types of Threat Intelligence?
Cyber Threat Intelligence is mainly categorized as strategic, tactical, technical, and operational.
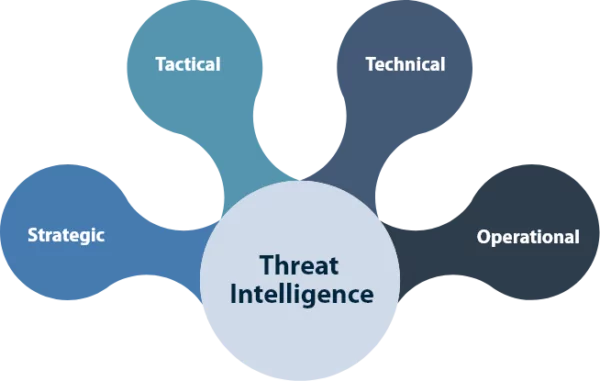
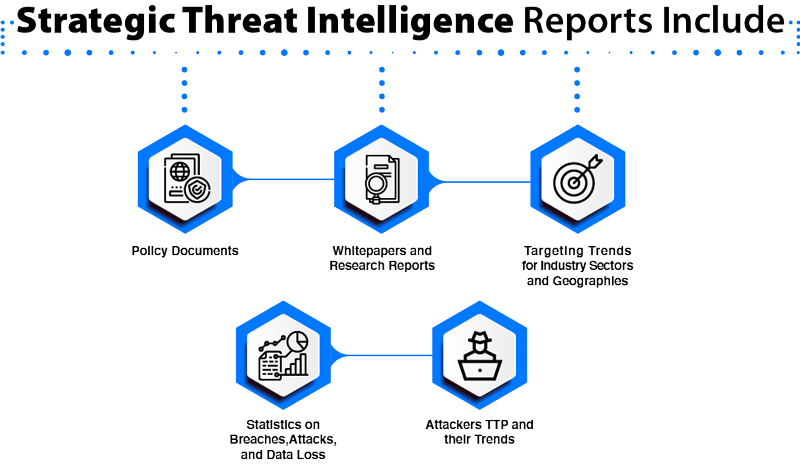
1. Strategic Threat Intelligence
Strategic threat intelligence provides an overview of the organization’s threat landscape. It is less technical is mainly for executive-level security professionals to drive high-level organizational strategy based on the findings in the reports. Ideally, strategic threat intelligence provides insights like vulnerabilities and risks associated with the organization’s threat landscape with preventive actions, threat actors, their goals, and the severity of the potential attacks.
2. Tactical Threat Intelligence
Tactical threat intelligence consists of more specific details on threat actors TTP and is mainly for the security team to understand the attack vectors. Intelligence gives them insights on how to build a defense strategy to mitigate those attacks. The report includes the vulnerabilities in the security systems that attackers could take advantage of and how to identify such attacks.
The finding is used to strengthen the existing security controls/defense mechanism and helps to remove the vulnerabilities in the network.
3. Technical Threat Intelligence
Technical threat intelligence focuses on specific clues or evidence of an attack and creates a base to analyze such attacks. Threat Intelligence analyst scans for the indicator of compromise (IOCs), which includes reported IP addresses, the content of phishing emails, malware samples, and fraudulent URLs. Timing for sharing technical intelligence is very critical because IOCs such as malicious IPs or fraudulent URLs become obsolete in a few days.
4. Operational Threat Intelligence
Operational threat intelligence focuses on knowledge about the attacks. It gives detailed insights on factors like nature, motive, timing, and how an attack is carried out. Ideally, the information is gathered from hacker chat rooms or their discussion online through infiltration, which makes it difficult to obtain.
Challenges in gathering operational Intelligence:
- Threats usually communicate over encrypted or private chat rooms, and access to these channels is not easy.
- It is not easy to manually gather relevant intelligence from huge data of chat rooms or other communication channels.
- Threat groups may use confusing and ambiguous language so that no one can understand their conversation.
Creating a Cyber Threat Intelligence Program
What is a Cyber Threat Intelligence Program?
How Do You Implement Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Golden Rules for Implementing a Cyber Threat Intelligence Program
- Create a Plan
- Involve the right people
- Understand the difference between Threat Data and Threat Intelligence
- Communication
- Know who all need the Intelligence
- Implement the right TTP (Tools, Techniques and Procedures)
- Integrate with the Organization security technology
Enterprise Objectives for Cyber Intelligence Programs
Role of Threat Analyst in Threat Intelligence Life cycle
Threat Intelligence Strategy and Capabilities
Threat intelligence strategy involves sound planning with the application of tools, techniques, and methodologies, followed by a review to check the effectiveness of the plan. While devising the strategy, one should also consider their threat intelligence capabilities and structure the program accordingly, including the support of different departments.
Cyber Threats and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
What are Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)?
Cyber Threat Intelligence Frameworks
Cyber threat intelligence framework creates intelligence to respond to cyber-attacks by managing, detecting, and alerting security professionals of potential threats. It provides an actional plan to mitigate the attacks by collecting the latest threat source information and create threat models.
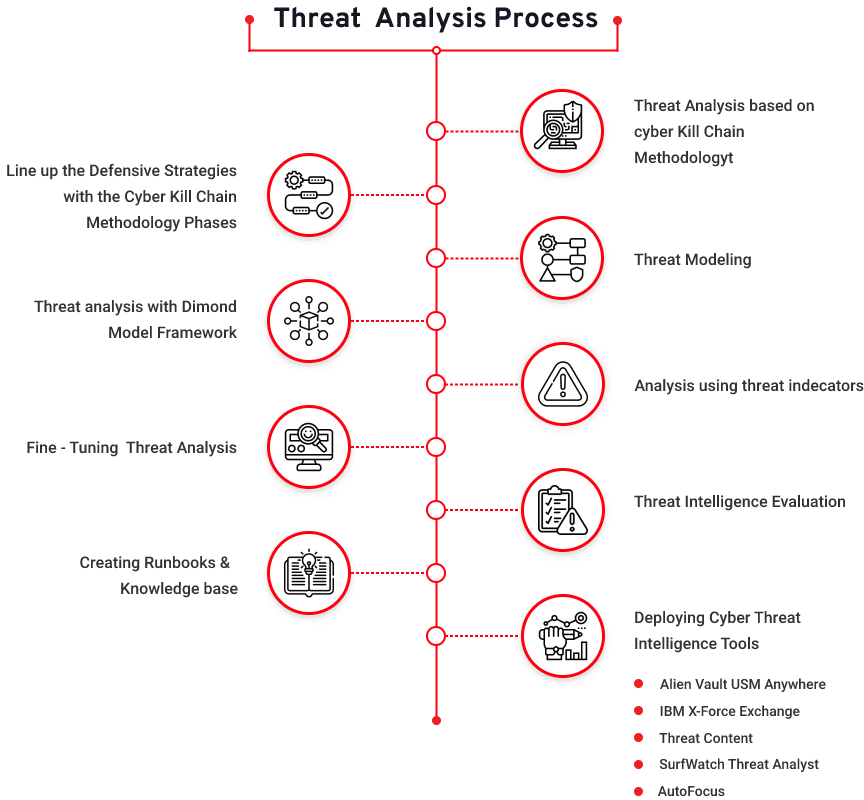
Understanding Cyber Kill Chain & IOCs
The cyber kill chain is a series of steps that trace stages of a cyberattack from the early reconnaissance stages to the exfiltration of data. The kill chain helps us understand and combat ransomware, security breaches, and advanced persistent attacks (APTs)
The cyber kill chain is a series of steps that trace stages of a cyberattack from the early reconnaissance stages to the exfiltration of data. The kill chain helps us understand and combat ransomware, security breaches, and advanced persistent attacks (APTs)
Organization’s Current Threat Landscape
This includes identifying critical threats to an organization, assessing the organization’s current security posture, security team’s structure, and competencies. Understanding of organization’s current security infrastructure and operations assist security professionals in assessing risks for identified threats.
Requirements Analysis
Requirement analysis is all about mapping organization’s ideal target state, identifying needs, and requirements for cyber intelligence, defining requirements and categories, aligning the requirements of business units, stakeholders and third parties, prioritizing intelligence requirements, the scope of cyber threat intelligence program, engagement rules, non-disclosure agreements, and common risks to cyber threat intelligence program.
Planning for a threat intelligence program
Establishing Management Support
Building a Threat Intelligence Team
Threat Intelligence Program Review
Threat Intelligence Data Collection & Processing
Cyber Threat Intelligence Data Collection and Acquisition
Collecting relevant threat data for analysis and processing is an important step for creating cyber threat intelligence. The data is collected from various sources using predefined TTP (Tactics, Techniques and Procedures). Few sources of data are internal like network logs, past cyber incidents, and security landscape. The external source includes threat feeds, communities, forums, open web, and dark web.
Cyber Threat Intelligence Feeds and Sources
What is A Threat Intelligence Feed?
What is A Threat Intelligence Feed?
TTP (Tactics, Techniques and Procedures) for Threat Data Collection
- Data Collection through Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) This includes data collection through open sources like Search Engines, Web Services, Website Footprinting, Emails, Whois Lookup, DNS Interrogation, and Automating OSINT effort using Tools/Frameworks/Scripts.
- Data Collection through Human Intelligence (HUMINT) This process involves data collection through Human-based Social Engineering Techniques, Interviewing, Interrogation, and Social Engineering Tools.
- Data Collection through Cyber Counterintelligence (CCI) In this step, threat data is collected through Honeypots, Passive DNS Monitoring, Pivoting Off Adversary’s Infrastructure, Malware Sinkholes, and YARA rules.
- Data Collection through Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) Collecting digital evidence data from internal sources, external sources, and creating custom threat IOCs.
- Data Collection through Malware Analysis Malware analysis is the process of understanding the origin and impact of a malware sample and how it functions by deploying analysis tools. Malware functions in multiple ways and gathers information about unsecured devices without the knowledge of the user.
Bulk Data Collection
Understanding Data Processing and Exploitation
Data Analysis
Data Analysis Techniques
- Statistical Data Analysis
- Analysis of Competing Hypotheses
Intelligence Reporting and Dissemination
How do you use cyber threat intelligence?
- Inform the security, professionals about the bad actors, potential threats, their methods, motive, and vulnerabilities organization are posed to.
- Help security professionals to be proactive about future cyber-attacks.
- Keep stakeholders informed about the latest threats and their impact on the business
- Help the security operations team to triage cyber-attacks, risk analysis, vulnerability management, and wide-scope decision making.
What is the future of threat intelligence?
According to a report by Grand View Research, Inc., the market for threat intelligence will reach $12.6 billion by 2025. This clearly shows the growing demand for cyber threat intelligence experts. In the future, there is enormous scope for threat intelligence services with the growing demand.
Companies, although investing generously in their cybersecurity solutions, remain susceptible to cyber-attacks, and this is an alert to help us realize that the traditional cybersecurity approach must be replaced with new and effective solutions, one of them is “cyber threat intelligence – a proactive approach to predictive analysis.”
A career in cyber threat intelligence has several number of avenues in the space of cybersecurity, and essentially there is a need for security professionals with skills in threat intelligence due to the evolving security landscape.
Cyber Threat Intelligence Jobs
Need for Threat Intelligence Analysts
How Much Does a Cyber Intelligence Analyst Make?
How Do You Become a Threat Intelligence Analyst?
What skills does an intelligence analyst need
Cyber Threat Intelligence Training
- Threat Data Collection
- Threat Data Analysis
- Threat Data Processing
- Hands-on with tools, techniques and procedures for threat data collection, analysis and processing
- Report Writting
- Threat Intelligence
Importance of Cyber Intelligence Training
Cyber Threat Intelligence Certification
Selecting a Cyber threat intelligence course
Frequently Asked Questions
EC-Council has a repository of learning resources and is not limited to the Threat Intelligence domain. Here is the list of resources, a). EC-Council Free Resources, b). EC-Council Blogs, c). EC-Council Whitepaper, d). EC-Council Cyber Talks