Digital Forensics Career Path
Master the Skills for:
Network Security | SOC Operations | Ethical Hacking Incident Handling | Forensics Investigation
Become a Digital Forensics Specialist
"*" indicates required fields
CERTIFIED PROFESSIONALS
IN 145 COUNTRIES







Digital Forensics Career Path
Master the Skills for:
Network Security | SOC Operations
Ethical Hacking | Incident Handling
Forensics Investigations
CERTIFIED PROFESSIONALS
IN 145 COUNTRIES






Become a Digital Forensics Specialist
"*" indicates required fields
Digital forensic science is a branch of forensic science that focuses on recovering and investigating material found in digital devices related to cybercrime. Digital forensics is identifying, preserving, analyzing, and documenting digital evidence. This is done to present evidence in a court of law when required.

What is DFIR (Digital Forensics Incident Response)?
Digital forensics and incident response (DFIR) focuses on finding, gathering, analyzing, and protecting electronic evidence to investigate and respond to cybersecurity incidents such as data breaches, malware infections, and other security violations. DFIR professionals play a crucial role in controlling and reducing cyber threats. The primary aspects of DFIR include:
Incident Handling & Response (IH & R): IH&R is a systematic response process for managing cybersecurity incidents. The goal is to minimize damage, reduce recovery time and costs, and investigate how the incident occurred.
Digital Forensics: The collection and analysis of digital evidence to uncover the details of a cyber incident. Digital forensics techniques examine computers, networks, and other digital devices to reconstruct events and determine the scope of a security breach.
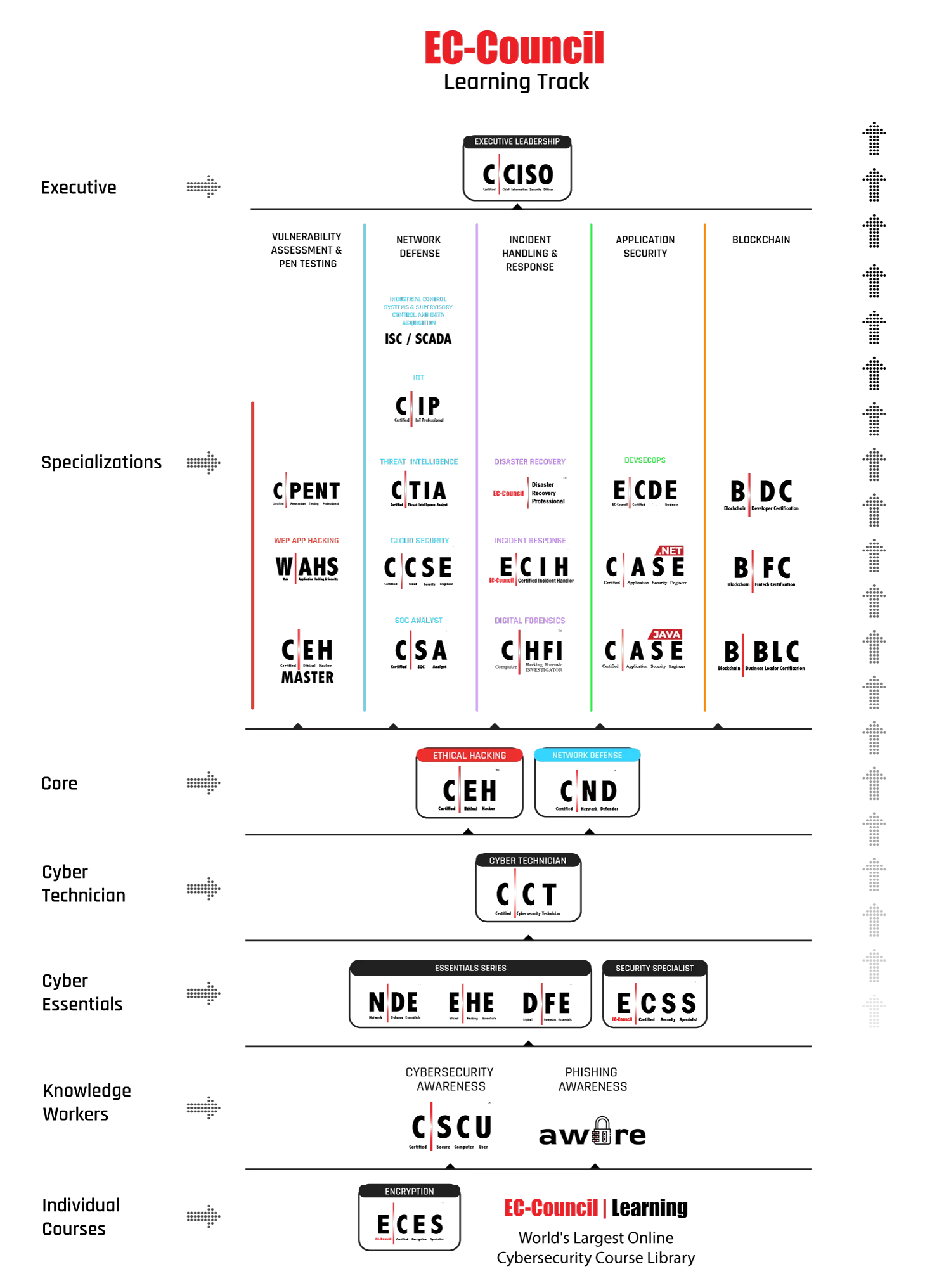
Your Pathway to a Digital Forensics Career
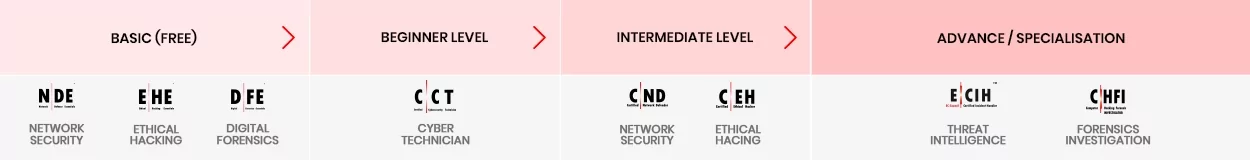
Key takeaways of above career path courses:
C|ND Course: Post CCT, you need to grow your career path with the Certified Network Defender certification. You will learn to examine network traffic at the binary level, master TCP/IP protocol, introduce vulnerability assessments and hacking methodology, and much more. These are essential skills that a VAPT professional should possess, a good foundation to become a network security expert.
C|EH Course: Once you have a solid foundation, you will be ready to move into ethical hacking with Certified Ethical Hacker (C|EH) course, Worlds No.1 Ethical hacking certification. C|EH learning framework Learn, Certify, Engage and Compete framework covers a comprehensive training program to prepare you for the certification exam and the industry’s most robust, in-depth, hands-on lab experience of any cybersecurity program available. The C|EH certification will help you get into the Hackers mindset and expose you to the 5 phases of ethical hacking, which will allow you to acquire the skills to become a competent professional in the Digital Forensics world.
Capstone Certification for Digital Forensics Career: C|HFI
Capstone Certification for DFIR: C|HFI + E|CIH
C|HFI Course: in the above section we have briefly described the C|HFI Course.
E|CIH Course: After mastering the 5 Phases of Ethical Hacking, you will be ready to learn how to detect, validate, contain, and eradicate security incidents with EC-Council Certified Incident Handling (E|CIH). This course addresses various underlying principles and techniques for detecting and responding to current and emerging cybersecurity threats.
Students will learn to master 8 stages in incident handling: Planning, Recording & Assignment, Triage, Notification, Containment, Evidence Gathering and Forensic Analysis, Eradication, Recovery, and Post-Incident Activities.
Students will learn the handling of various types of incidents, risk assessment methodologies, and laws, policies related to incident handling. After attending the course, students can create IH&R policies and deal with different types of security incidents, such as malware, email security, network security, web application security, cloud security, and insider threat-related incidents.
Digital Forensics Skills Are Rare
Demand for Digital Forensics Professionals Continue to Rise
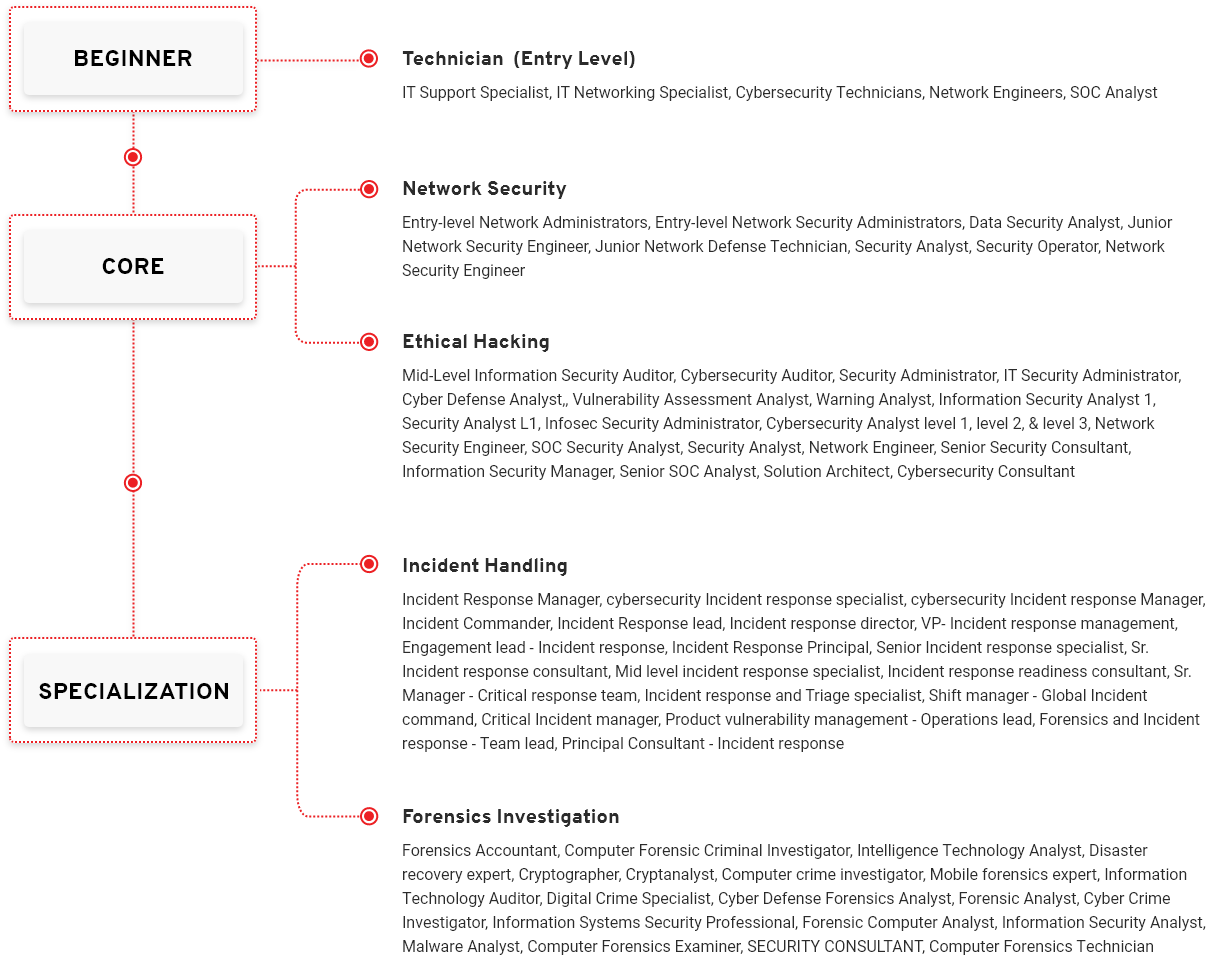
Job Roles Mapped to Digital Forensic Career Path
Job Roles Mapped to Application Security Career Path
Entry-level Network Administrators, Entry-level Network Security Administrators, Data Security Analyst, Junior Network Security Engineer,
Junior Network Defense Technician, Security Analyst, Security Operator, Network Security Engineer
Incident Response Manager, cybersecurity Incident response specialist, cybersecurity Incident response Manager, Incident Commander,
Incident Response lead, Incident response director, VP- Incident response management, Engagement lead – Incident response, Incident
Response Principal, Senior Incident response specialist, Sr. Incident response consultant, Mid level incident response specialist, Incident
response readiness consultant, Sr. Manager – Critical response team, Incident response and Triage specialist, Shift manager – Global
Incident command, Critical Incident manager, Product vulnerability management – Operations lead, Forensics and Incident response –
Team lead, Principal Consultant – Incident response
7 Reasons to choose Digital FORENSICS Career Path
Accreditations : C|ND, C|HFI, and C|EH courses are ANSI Accredited, and DoD (US. Department of Defense) Approved.
A Digital Forensics Specialist can
Decode an Attack. Compile Evidence.
Prosecute Criminals. Defend Organizations.
Accreditations, Recognitions & Endorsements